What is Conversational AI?
Conversational AI is an umbrella term
used to describe various methods of enabling computers to carry on a
conversation with a human. This technology ranges from fairly simple natural
language processing (NLP) to more sophisticated machine learning (ML) models
that can interpret a much wider range of inputs and carry on more complex
conversations.
One of the most common applications
of conversational AI is in chatbots, which use NLP to interpret user
inputs and carry on a conversation. Other applications include virtual
assistants, customer service chatbots, and voice assistants.
Savvy consumers expect to communicate
via mobile app, web, interactive voice response (IVR), chat, or messaging
channels. They look for a consistent and enjoyable experience that’s fast,
easy, and personalized.
For businesses, the key to meeting and
exceeding these expectations across channels and at scale is intelligent
automation. Conversational artificial intelligence (AI) powers interactions
that are near human, improving CX, boosting satisfaction, driving loyalty, and
increasing customer lifetime value (LTV).
Components of Conversational AI
Conversational AI can be broken down
into five core components. These five core components work together to enable a
computer to understand and respond to human conversation:
1. Natural language processing
NLP is the ability of a computer to
understand human language and respond in a way that is natural for humans. This
involves understanding the meaning of words and the structure of sentences, as
well as being able to handle idiomatic expressions and slang.
NLP is made possible by machine
learning, which is used to train computers to understand language. NLP
algorithms use large data sets to learn how words are related to each other,
and how they are used in different contexts.
2. Machine learning
Machine learning is a field of
artificial intelligence that enables computers to learn from data without being
explicitly programmed. Machine learning algorithms can automatically improve
their performance as they are exposed to more data.
Machine learning is used to train
computers to understand language, as well as to recognize patterns in data. It
is also used to create models of how different things work, including the human
brain.
3. Text analysis
Text analysis is the process of
extracting information from text data. This involves identifying the different
parts of a sentence, such as the subject, verb, and object. It also includes
identifying the different types of words in a sentence, such as nouns, verbs,
and adjectives.
Text analysis is used to understand the
meaning of a sentence, as well as the relationships between different words. It
is also used to identify the topic of a text, as well as the sentiment
(positive or negative) of the text.
4. Computer vision
Computer vision is the ability of a
computer to interpret and understand digital images. This involves identifying
the different objects in an image, as well as the location and orientation of
those objects.
Computer vision is used to identify the
contents of an image, as well as the relationships between different objects in
the image. It is also used to interpret the emotions of people in photos, and
to understand the context of a photo.
5. Speech recognition
Speech recognition is the ability of a
computer to understand human speech. This involves recognizing the different
sounds in a spoken sentence, as well as the grammar and syntax of the sentence.
Speech recognition is used to convert
spoken words into text, and to understand the meaning of the words. It is also
used to interpret the emotions of people speaking in a video, and to understand
the context of a conversation.
How Does Conversational AI Work?
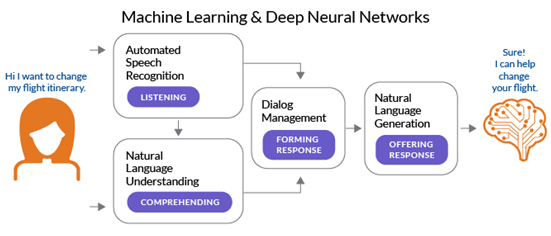
Driven by underlying machine learning
and deep neural networks (DNN), a typical conversational AI flow includes:
An interface that allows the user to
input text into the system or Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), a user
interface that converts speech into text.
Natural language processing (NLP) to
extract the user's intent from the text or audio input, and translate the text
into structured data.
Natural Language Understanding (NLU) to
process the data based on grammar, meaning, and context; to comprehend intent and
entity; and to act as a dialogue management unit for building appropriate
responses.
An AI model that predicts the best
response for the user based on the user's intent and the AI model's training
data. Natural Language Generation (NLG) infers from the above processes, and
forms an appropriate response to interact with humans.
In many cases, the user interface, NLP,
and AI model are all provided by the same provider, often a conversational
AI platform provider. However, it's is also possible to use different providers
for each of these components.
 How to create Conversational AI?
How to create Conversational AI?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to
this question, as the best way to create conversational AI depends on the
specific needs and use cases of your organization. However, some tips on how to
create conversational AI include:
1. Start by
understanding your use cases and requirements.
The first step in creating
conversational AI is understanding your organization’s specific needs and use
cases. What are you trying to achieve with your chatbot? What type of
conversations do you want it to be able to have? What data do you need to
collect and track? Defining these requirements will help you determine the best
approach to creating your chatbot.
2. Choose the right platform and toolkit.
There are a number of different
platforms and toolkits that you can use to create conversational AI. Each
platform has its own strengths and weaknesses, so you need to choose the
platform that best suits your needs. Some popular platforms include [24]7.ai
Conversations, Microsoft Bot Framework, Amazon Lex, Google Dialogflow, and IBM
Watson.
3. Build a prototype.
Once you have defined your requirements
and chosen a platform, it’s time to start building your prototype. Building a prototype
will help you test your chatbot and iron out any kinks before deploying it
to your users.
4. Deploy and test your chatbot.
Once your prototype is finished, it’s
time to deploy and test your chatbot. Make sure to test it with a small group
of users first to get feedback and make any necessary adjustments.
5. Optimize and improve your chatbot.
The final step is to continually
optimize and improve your chatbot. You can do this by tweaking the algorithms,
adding new features, and collecting user feedback.
Implementing Conversational AI
There are a number of ways to implement
conversational AI. The most common way is to use natural language processing
(NLP) to convert text into machine-readable data. This data can then be used to
power a chatbot or other conversational AI system.
NLP, as noted earlier, is a process of
understanding human language and using that understanding to convert text into
a format that a computer can understand. This process can be used to interpret
questions and commands from users, as well as to analyze and respond to user
feedback.
There are a number of different approaches to NLP. Some systems use machine learning to train a computer to understand natural language. Others use a rules-based approach, where a human editor creates a set of rules that define how the computer should interpret and respond to user input.
Once the computer has been trained or
has been given a set of rules, it can then use this information to power a
chatbot or other conversational AI system. This system can be used to handle
customer support inquiries, answer questions, and carry out other tasks that
would traditionally require human interaction.
What is Conversation Design and Why Does Conversational AI Need It?
Many tools are now available for
building chatbots and speech bots that deliver automated conversation
development, however, conversation design is not straightforward and
remains a human-led discipline.
In customer service, the ability to
resolve requests at a high rate and satisfaction level is critical. Successful
resolution depends on intent determination and intent handling. To understand
intent better, machine learning (ML) models are trained on actual
conversations. That conversational data is tagged by human analysts and contact
center agents, and augmented with signals including behavioral (for example,
prior web pages viewed), enterprise (order status), and external (local
weather/events). This makes for smarter intent prediction and faster
resolution.
Unsupervised ML techniques are also used
to mine customer-agent conversations to determine common dialogue flow
patterns. The sample set of conversational data used for model training is
chosen from top-notch agents, as determined by resolution rates and customer
satisfaction ratings. Identified flows then give conversation designers a much
better starting point for writing dialogues.
Conversations often contain more than
one intent. To fully automate an interaction, conversation designers must
incorporate intent sequences into their bot design. If the bot is unable to
handle the second and subsequent intents, the customer will have to escalate to
a human agent—which increases the cost of the interaction. And if a human agent
isn’t available, the customer is left with a partially complete
interaction—which is probably worse than no interaction at all.
Conversational AI technologies depend on
an intent-driven conversation design to deliver solutions for specific use
cases such as customer support, IT service desk, marketing, and sales support.
Conversational AI also offers integration with chat interfaces in SMS,
web-based chat, and other messaging platforms.
Explore how to design
conversational AI chatbots and remember, thoughtful conversation design is
a key component
for success and the ability to turn visitors into engaged customers.
Learn why conversational AI is essential for your business.
Video: Learn More About Conversational AI
Conversational AI and Chatbot
Differences
When we speak about automated
human-computer digital interactions, the line between chatbots and
conversational AIcan start to blur. Oftentimes, the terminologies have been
used interchangeably.
Is conversational AI different from a chatbot?
To begin with, let’s look at how they’re
connected at a fundamental level:
Conversational AI encompasses a set of
foundational technologies for developing chatbots. In other words, an
intelligent chatbot is an application that’s built based on a conversational AI
platform.
Nevertheless, not all chatbots are based
on conversational AI technologies. In fact, a large proportion of chatbots are
human scripted and/or rule-based—and not conversational at all. These bots can
only produce one-time responses, aren’t interactive, and perform barely one
step above an old-school IVR system.
Chatbots, virtual personal assistants,
automated messaging systems, agent-assisting bots, and AI-powered FAQ bots, are
all types of applications built on conversational AI platforms.
Conversational AI brings together a
range of advanced capabilities for an omnichannel UI, contextual awareness,
language processing, response generation, intent management,
exception/escalation management, advanced analytics, and integration.
A chatbot, on the other hand, is a
computer application that simulates human conversation through voice commands,
text input, or both. Chatbots make it easy for users to find the information
they need in real time, automate responses to user queries, and can complete
tasks without the need for human intervention.
Chatbots support a range of digital (for
example, messaging apps, mobile apps, website) and voice channels (IVR, smart
speakers) to offer both customers and employees a conversational, self-serve
experience at scale.
The name chatbot, short for chatterbot,
is also often used interchangeably with bot, virtual assistant, AI chatbot,
conversational agent, and talkbot.
Want to deep dive into the different type of chatbots?
Start here: All About AI-Powered
Chatbots.
Conversational AI contains components
that allow it to capture user inputs; break down, process, and understand them;
and generate a meaningful response in a natural way—all within microseconds.
This is possible because conversational AI combines NLP with machine learning
(ML) to continuously improve the AI algorithms.
For convenience, let’s bundle scripted
and rule-based chatbots together and call them “traditional chatbots”. So,
there are traditional chatbots and AI-powered chatbots. Here’s a side-by-side
comparison of the two:
|
Traditional chatbots |
AI-powered chatbots |
|
|
Basic answer and response machines Allow for simple integration Based on limited scope Need explicit training for every
scenario (not “intelligent”) Require low back-end effort |
Can manage complex dialogues Integrate with multiple
legacy/back-end systems Based on larger scope Specialize in completing tasks
interacting with multiple systems Require high back-end effort |
Goes beyond conversations Contextually aware and intelligent Can self-learn and improve over time Can anticipate user needs Require massive back-end effort |
For more on this topic, check out the blog: Conversational AI and Chatbots: How We Got Here.
[24]7.ai Conversational AI Differentiators
Conversational AI Challenges
Conversational AI’s maturity has
steadily increased over the past few years to the point where it can now
deliver excellent business value and outcomes for companies. Nevertheless,
challenges abound since this is also a fast-evolving conversational
commerce category where very few vendors are constantly innovating and
bringing new technologies to the market. Challenges include:
Developing natural language processing
(NLP) capabilities that can understand and interpret human interactions. This
is a complex task that requires significant effort and investment in research
and development.
Understanding the context of a
conversation in order to provide accurate responses. This can be particularly
challenging in conversations that involve multiple people or multiple topics.
The need for sophisticated design and
development efforts to create a customer experience that engages users and
keeps them engaged in the conversation.
Deploying and integrating a
Conversational AI solution into an existing business or application can be a
significant challenge. Proper planning and execution are essential to ensure a
successful deployment.
Ensuring the security and privacy of
data exchanged via multiple conversational AI-powered channels—this applies to
any CX-related information exchange. Compliance with standards such as GDPR,
CCCP, and other country-specific regulations is also critical.
As conversational AI permeates global CX
platforms, local language support becomes a high priority. Leading brands
operating worldwide can’t rely on availability in just one language to meet
local needs at scale. Building a robust conversational AI platform to operate
in regional languages, dialects, slang, noisy environments, with crosstalk,
etc., is a huge challenge.
Dialogue management and conversation
design are non-trivial parts of conversational AI. Annotating the intelligence
gathered from real agent conversations and building the right model-training
data requires ongoing human-in-the-loop expertise.
Building a conversational AI-based
application that takes into consideration intent, entity extraction, sentiment
analysis, and empathy is challenging and very few vendors offer solutions with
these features.
Explainable AI—not all conversational AI
platforms use this data science tool, which eliminates algorithmic black boxes and
helps answer the “why” within the model’s functionality. Explainable AI also
improves trust in the platform’s ability to produce accurate, fair, and
transparent results.
Keeping automated conversations relevant
can also be a real challenge, with customer needs and preferences changing
faster than ever before. As a result, you may need people with coding
skills, multiple-persona models, or IT input, making the solution more
expensive. Conversational AI platforms that have no-code/low-code self-serve
capabilities can enable business users to build and deploy voice and digital
bots and context-aware conversational flows in just a few days.
Improve CX with Conversational Commerce
State-of-the-Art Conversational AI
Technology behind conversational bot
experiences is based on the latest advances in artificial intelligence, NLP,
sentiment analysis, deep learning, and intent prediction. Together, these
features encourage engagement, improve customer experience and agent
satisfaction, accelerate time to resolution, and grow business value.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Most conversational AI uses NLU to
intelligently process user inputs against multiple models, enabling a bot to
respond in a more human-like way to non-transactional journeys. The core
technology understands slang, local nuances, colloquial speech, and can be
trained to emulate different tones by using AI-powered speech synthesis.
Sentiment Analysis
This leading conversational AI
technology layer abstracts pre-built sentiment and social models to prioritize
and seamlessly escalate to an agent when it detects that a customer needs
expert advice. Sentiment detection will recognize, for example, an upset
customer and immediately route them to an agent. You can also prioritize
unhappy customers in the system, placing them in special queues or offering
exceptional services.
Deep Learning
This machine learning technique is
inspired by the human brain or ‘neural network’ and allows AI to learn by
association, just like a child. The more data AI is exposed to, the better it
gets—and the more accurately it can respond over time. AI models trained with
many years of contact center data from various voice and digital channels
result in smarter and more accurate responses to human inquiries. Response
accuracy can be further improved over time by learning from interactions
between customers, chatbots, and human agents, and optimizing intent models
using AI-powered speech synthesis.
Intent Prediction
Using behavioral analysis and tagging
activities, conversational AI technologies can understand the true meaning
behind each consumer’s request. Knowing intent allows companies to deliver the
right response at the right moment through an automated bot or human agent.
The future roadmap for conversational AI
platforms includes support for multiple use cases, multi-domain, and multiple
vertical needs, along with explainable AI.
The Conversational AI Vendor Market
According to Gartner™, over 1500 conversational
AI providers now offer various levels of capability, language support,
use-cases, and business models.
Sophistication swings widely depending
on what’s supported, such as:
Number of integrations with back-end
systems such as CRM
Number and type of channels (voice,
text-based chatbots, messaging, etc.).
Customization of chatbots and virtual
assistants for vertical specific use cases and applications for faster adoption
into production
Number of languages, slang, dialects,
local lingo, shorthand, phonetic spelling, grammatical structures, intents,
entity, etc.
Horizontal solutions are the most
flexible and controllable but take longer to implement, while vertical specific
ones come with pre-built capabilities that are a better fit for a specialized
use cases in a target domain. Vendors that offer vertical solutions built on an
established horizontal platform give companies full flexibility in customizing
to meet their precise needs.
According to Gartner, the
conversational AI platform market is predicted to grow 75% year-over-year from
about $2.5 billion in 2020. Platform vendors now provide differentiated value
to businesses with advanced functionality that supports automated intent and
entity detection, smaller training datasets, human-in-the loop tools for
annotation and conversation design, and a low-code/no-code paradigm for
non-technical people to build smart chatbots and virtual assistants.
How to pick the right Conversational AI Solution?
When it comes to selecting a
conversational AI solution, there are a few key factors to consider.
First, consider the needs of your
business. What questions or tasks do your customers commonly ask or need help
with? What areas of your business could benefit from automation?
Next, evaluate the capabilities of
different conversational AI solutions. Some platforms are better suited for
specific tasks or industries, while others are more versatile.
Finally, consider the cost and
complexity of implementing different solutions. Some platforms are more
expensive or require more technical expertise to set up and use.
Once you have a better understanding of
your business needs and the capabilities of different conversational AI
solutions, you can begin to narrow down your options and select the right
platform for your business.
The [24]7.ai Conversational AI
Difference
[24]7 AIVA™ Conversational AI is a
technology layer that combines the world’s most advanced NLP technology with an
intent-driven engagement platform to enable ‘near-human’ conversations in
digital and voice channels. AIVA understands slang, local nuances, and
colloquial speech, and can be trained to emulate different tones by using
AI-powered speech synthesis.
Consistent brand experiences:
omnichannel orchestration: Consumers today use more devices and channels
than ever. With AIVA, you can let them choose when, where, and how to connect
with your brand and ensure a familiar experience wherever they are—including
digital, voice, and messaging channels. With AIVA at the core, the experience
is seamless and consistent at every touch point.
AI with emotional intelligence:
sentiment analysis and social detection: Unlike most AI platforms, AIVA
can detect when a customer is upset and prioritize service by escalating them
to a live agent. This emotional intelligence (EQ) paired with advanced NLP
helps you understand what your customers mean, not just what they say. Plus,
social models give chatbots or virtual assistants personality—because automated
interactions that feel more human make a big difference to customer
satisfaction.
Continuous improvement: deep learning
technology: AIVA combines deep learning technologies with our unique
collaborative tagging to self-learn and evolve, bringing ever smarter and more
accurate automation into the equation. We start with AI models trained on two
decades of contact center expertise and add technology that enables the AI to
learn by association. AIVA uses interactions between customers, bots, and
agents to learn and improve continuously.
Smart to collaborate with a human
agent: Handing off a conversation to a human agent is just the beginning. AIVA
conversational AI uniquely enables virtual assistants that can retrieve one
piece of data from a human agent while the customer waits briefly. Once AIVA
gets what it needs, it continues the dialogue. The customer gets served and the
increased ability boosts containment by leveraging the best of human agents and
machine intelligence.
Support for asynchronous
messaging: Messaging has transformed the way people keep in touch with
each other in their day-to-day lives, and now it’s changing the way they interact
with brands as well. The ability to carry on conversations asynchronously is a
game changer for companies and consumers alike. AIVA powers conversational AI
across messaging channels to meet your customers where they are, boosting
satisfaction and loyalty. Powering every interaction with AIVA enables
conversational AI clients to deliver superior experiences, control operational
costs, and elevate outcomes. It’s better for customers, better for agents, and
better for business.
Transforming customer service with conversational AI
Control operational costs by automating
conversations
Anticipate customer intent and
accelerate resolution
Drive digital transformation and
self-service containment
Boost customer satisfaction by
delivering superior experiences
Increase agent productivity and reduce
average handle time (AHT)
Reach key global markets with support
for multiple language
To find out how [24]7.ai’s leading
conversational AI technology can change the game for your automated customer conversations, contact us today.
4 Methods to Blend AI and Human Agents in Your Contact Center
No comments:
Post a Comment